In 1973, the world broke out the first oil crisis, Japan's economy fell into chaos, the economic growth rate dropped sharply in 1974, the post-war high economic growth came to an end. The main export products have changed from steel to automobiles. After the 1970s, Japan maintained a huge trade surplus for a long time, while the United States ran a long-term trade deficit. Since then, under the plaza accord, the yen has had to rise, causing economic distress. After the 1980s, the boom continued to be strong due to loose financial conditions, leading to sharp rises in stock prices and land prices. Bubble economy. In the 1990s, asset prices (stock prices, land prices) fell sharply, and Japan's prolonged economic downturn was considered as the "lost decade" due to the aftermath of the collapse of the bubble economy. Since 2002, the situation has improved, led by rising foreign demand. In the 1990s, asset prices (stock prices, land prices) fell sharply, and Japan's prolonged economic downturn was considered as the "lost decade" due to the aftermath of the collapse of the bubble economy. Since 2002, the situation has improved, led by rising foreign demand. Japan's economy shrank in the third quarter for the first time since last year, plunging the world's third-largest economy into recession and prompting the bank of Japan to announce it would continue its strong monetary stimulus to boost growth. But economists say domestic stimulus is unlikely to pull Japan out of recession because its recovery depends more on global growth.


At present, the Japanese economy faces the following problems:
Japan's economy suffered a devastating blow in the second world war. But it recovered quickly after the defeat. At present, if calculated according to the international exchange rate, its GDP ranks the third in the world, and it is one of the world's major economic powers. Japan is now the world's third largest economy, after the United States and China. After the bubble economy, the growth rate did not recover. In the early 21st century, there was a recovery. However, the unemployment rate did not drop significantly.
At present, Japan's economic growth has initially shown signs of stabilizing and picking up after an unexpected decline. However, both domestically and internationally, Japan faces a mixed situation, and the pressure on growth cannot be ignored. In general, the Japanese economy will show a small recovery in 2019 and maintain a medium-low growth trend. The next phase of the Japanese economy, while unlikely to slip into recession, is likely to face headwinds.
5.The gap between rich and poor. The common problems of capitalism also happened in Japanese society; From the original middle class as the mainstream of society, to the rich and poor extremes (the middle class gradually disappear). In his book the m-shaped society, kenichi ohma discusses the strange phenomenon in Japan, which may come from globalization and industrial upgrading structure. People in the lower middle class are impacted, while the rich class is not impacted or even benefited from it, which leads to the widening of the class and the cultural phenomena such as the collapse of values and workplace ethics.
6.Public debt is huge. With Japanese public debt at 832 trillion yen ($7 trillion), or about 170 percent of GDP, since 2006, yubari on Hokkaido has become the first municipal authority in Japan to declare bankruptcy because of overspending.
1. Hollowing out the industry. After the 1980s, many factories moved overseas due to higher labor costs caused by the appreciation of the yen, leading to the hollowing out of the industry. In recent years, some companies have set up research and development centers and production bases in Japan to prevent technology outflow and stay competitive. Many advocate moving companies back to Japan.
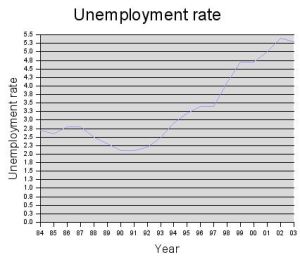
3.Starting a business is difficult. Entrepreneurship is more difficult than Europe and the United States in Japan. To explore the reason, many people will name because can only borrow money from
2. Financial inefficiency. During the bubble, the value of real collateral (property and land) collapsed as a result of excess financing. As a result, Banks have been saddled with huge bad debts so far.
4.Financial agencies in Japan. No experience to borrow money from financial organ was pretty difficult. Even borrow, the interest rate is also high. One thousand start-up failure is necessary with massive debt. Aiming at this problem, the Japanese government in 2004 amendment, establish the yuan can startup and a variety of business support system. But the effect is unknown.
(Picture Source:Baidu)
The biggest driver of Japan's economy should be global demand, particularly in the us, China and Europe. Without an increase in external demand, neither the government nor the central bank would have done enough to prevent a recession. Japan's development over the past few decades shows that its economy is highly dependent on exports and external demand. As a result, Japan has to wait for overseas economic recovery to boost its own economy.


